How to operate a drone? It’s more than just pushing buttons; it’s about mastering a sophisticated piece of technology while adhering to safety regulations and best practices. This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough, from pre-flight checks and understanding drone controls to mastering aerial photography and ensuring legal compliance. We’ll cover everything you need to know to become a confident and responsible drone pilot.
From understanding the nuances of flight modes and navigating with GPS waypoints to optimizing camera settings for stunning aerial shots, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to operate your drone safely and effectively. We’ll also delve into essential maintenance, battery care, and legal considerations to ensure your drone operation remains compliant and trouble-free.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting all key components and confirming adherence to safety regulations. Failure to do so can lead to accidents, damage, or legal issues.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection is paramount to safe operation. The following table details essential checks:
| Component | Inspection Item | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Visual inspection for cracks, chips, or damage | No visible damage; securely fastened | Cracks, chips, or bends; loose or damaged |
| Battery | Battery level and condition | Sufficient charge; no visible damage or swelling | Low charge; visible damage or swelling |
| Gimbal | Smooth movement and stability | Moves freely and smoothly; no unusual noises | Stiff movement; unusual noises or vibrations |
| Camera | Lens clarity and functionality | Lens clean and clear; camera functions correctly | Dirty or scratched lens; camera malfunctioning |
Essential Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Responsible drone operation requires adherence to specific safety regulations and best practices. Ignoring these can have serious consequences.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Never fly near airports, airfields, or other restricted airspace.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Fly only in suitable weather conditions – avoid strong winds, rain, or snow.
- Be aware of surrounding obstacles and avoid collisions.
- Keep your drone’s battery charged and in good condition.
- Regularly inspect your drone for any damage or wear and tear.
- Familiarize yourself with local drone regulations and obtain necessary permits.
Safe Flight Conditions Decision-Making Process
A flowchart would visually represent the decision-making process for determining safe flight conditions. This would involve checking weather conditions, airspace restrictions, battery level, and drone status before proceeding with the flight.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to safely and effectively handle your drone is crucial, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This will help you gain confidence and proficiency in piloting your drone, ultimately leading to a better understanding of its capabilities and limitations.
The flowchart would start with checking weather (wind speed, precipitation), proceed to checking airspace restrictions (no-fly zones, airport proximity), then check battery level and drone health (propellers, sensors). Each check would lead to a “yes” or “no” decision, ultimately resulting in a “safe to fly” or “unsafe to fly” conclusion.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning to safely and effectively handle a drone is crucial, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This guide covers everything from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques, ensuring you’re well-equipped to confidently operate your drone.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial. Loss of signal or malfunction are common scenarios requiring swift action.
- Loss of Signal: Immediately activate the “Return to Home” (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, attempt to manually regain control. If still unsuccessful, locate the drone visually and recover it safely.
- Malfunction: Assess the nature of the malfunction. If it’s a minor issue (e.g., a minor software glitch), attempt a restart. For more serious problems (e.g., motor failure), immediately land the drone safely. If the drone is uncontrollable, prioritize safety and avoid potential damage or injury.
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Understanding your drone’s controls and flight modes is essential for safe and effective operation. Different modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios.
Drone Remote Control Functions
A typical drone remote controller features two control sticks and several buttons. The left stick controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick manages roll (tilt) and pitch (forward/backward movement). Buttons typically include power, camera controls, and flight mode selection.
A labeled diagram would show the left stick (up/down for altitude, left/right for yaw), the right stick (left/right for roll, forward/backward for pitch), and buttons for power, camera, RTH, and flight mode selection.
Comparison of Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and control. Choosing the right mode is crucial based on your experience and the complexity of the flight.
| Flight Mode | Stability | Control | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner | High | Limited | New pilots; practicing basic maneuvers |
| Sport | Medium | High | Experienced pilots; dynamic maneuvers |
| Acrobatic (if available) | Low | Maximum | Highly experienced pilots; complex stunts |
Drone Compass and Sensor Calibration

Regular calibration ensures accurate flight and positioning. This involves setting the drone’s internal compass and other sensors to match its real-world orientation.
- Power on the drone and remote.
- Place the drone on a flat, level surface, away from metal objects and electronic interference.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibrating the compass and other sensors. This typically involves rotating the drone slowly in a figure-eight pattern.
- Confirm successful calibration through the drone’s app or display.
Tips for Smooth Drone Maneuvers
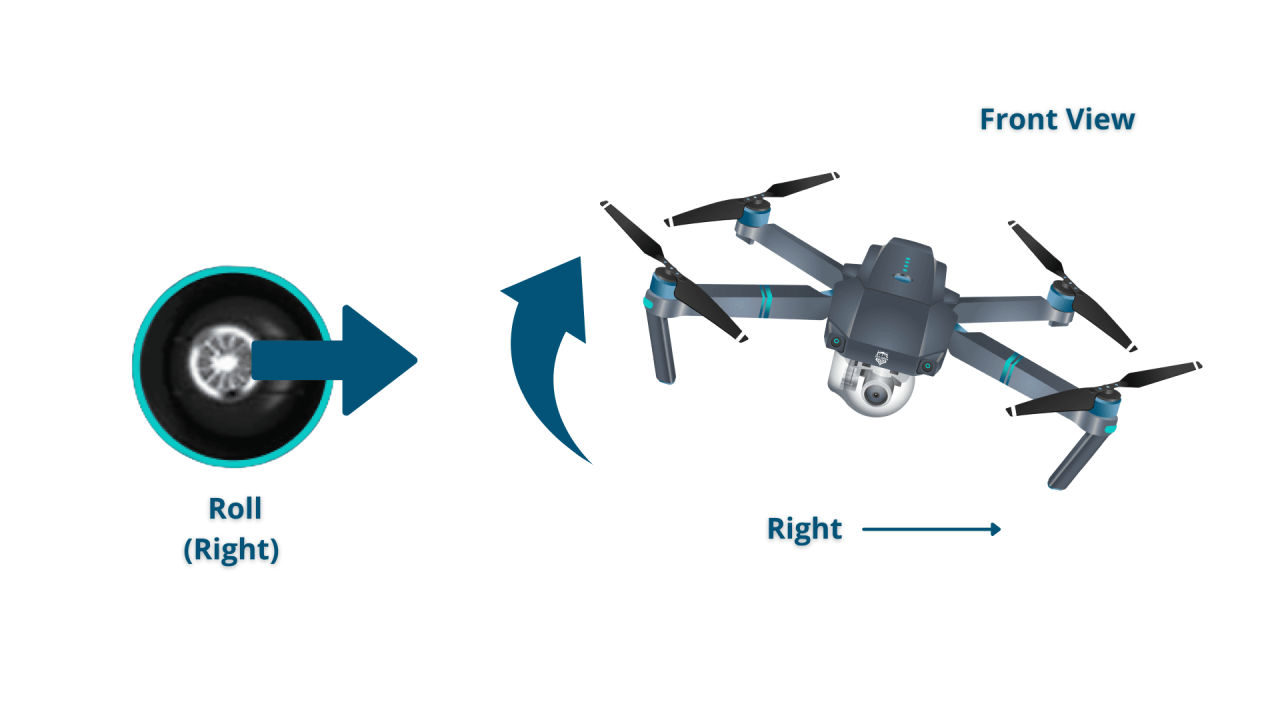
Smooth and controlled maneuvers require practice and understanding of the drone’s responsiveness. Mastering these techniques enhances flight safety and image quality.
- Takeoff: Initiate takeoff slowly and smoothly, allowing the drone to gain stability before making any significant movements.
- Landing: Approach the landing area slowly and gently lower the drone to the ground, ensuring a smooth and controlled descent.
- Hovering: Practice maintaining a steady hover by making small, precise adjustments to the control sticks.
Navigation and Flight Planning
Effective navigation and flight planning are essential for safe and efficient drone operations, especially in complex environments.
Drone Navigation Methods
Drone navigation can be achieved through various methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- GPS Waypoint Navigation: Pre-programmed waypoints guide the drone along a defined path, simplifying complex flights and ensuring consistent coverage. This method is suitable for tasks like aerial photography or surveying.
- Manual Control: Direct control of the drone’s movement using the remote controller. This offers maximum flexibility but requires greater skill and attention.
Sample Flight Plan, How to operate a drone
A sample flight plan Artikels the intended flight path, including waypoints, altitudes, and speeds. This helps ensure a structured and safe flight.
| Waypoint | Latitude | Longitude | Altitude (meters) | Speed (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 34.0522° N | 118.2437° W | 50 | 5 |
| 2 | 34.0530° N | 118.2445° W | 50 | 5 |
| 3 | 34.0538° N | 118.2437° W | 50 | 5 |
Impact of Wind Conditions
Wind significantly impacts drone flight, affecting stability and control. Understanding wind conditions is crucial for safe operation. Strong winds can make it difficult to control the drone, potentially leading to accidents.
Obstacle and Hazard Avoidance
Identifying and avoiding obstacles and hazards is critical for safe drone operation. This involves careful pre-flight planning, visual observation during flight, and using the drone’s obstacle avoidance features (if available).
- Visual Inspection: Thoroughly scan the flight area for potential hazards before takeoff.
- Obstacle Avoidance Systems: Utilize the drone’s built-in obstacle avoidance sensors to detect and avoid obstacles automatically.
- Safe Altitudes: Maintain sufficient altitude to clear obstacles and avoid collisions.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for photography and videography. Mastering camera settings and composition techniques is key to capturing high-quality aerial media.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Optimizing camera settings for various lighting conditions is crucial for achieving the desired image quality.
- Aperture: Controls depth of field; a wider aperture (lower f-number) creates a shallower depth of field, blurring the background.
- Shutter Speed: Controls motion blur; a faster shutter speed freezes motion, while a slower shutter speed can create a sense of movement.
- ISO: Controls sensitivity to light; a lower ISO reduces noise but requires more light, while a higher ISO increases noise but allows shooting in low light.
Camera Angles and Shots
Drones allow for a variety of creative camera angles and shots.
- High-angle shots: Capture a broad overview of the scene.
- Low-angle shots: Emphasize size and scale.
- Tracking shots: Follow a subject as it moves.
- Orbiting shots: Circle a subject, revealing its surroundings.
Tips for Composing Aerial Shots
Composition is key to compelling aerial photography and videography. Understanding the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques enhances the visual appeal of your work.
Transferring Footage
Transferring footage from the drone to a computer typically involves using a microSD card reader or connecting the drone directly to the computer via a USB cable. The specific method depends on the drone model and its software.
Drone Maintenance and Battery Care
Regular maintenance and proper battery care are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring safe operation.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule helps prevent malfunctions and extends the drone’s lifespan.
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visual inspection for damage | Before each flight |
| Cleaning propellers and body | After each flight |
| Thorough cleaning and inspection | Monthly |
| Firmware update | As needed |
Proper Battery Care
Proper battery care is essential for optimal performance and safety.
- Charging: Use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow charging instructions carefully.
- Storage: Store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Safety: Never leave batteries unattended while charging.
- Calibration: Calibrate the battery periodically according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Understanding common drone malfunctions and troubleshooting steps allows for quick resolution of issues. This can include problems such as motor failure, GPS signal loss, or camera malfunction.
Replacing Damaged Parts
Replacing damaged parts, such as propellers, is a straightforward process. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific guidance. This often involves removing the damaged part and securely attaching a replacement.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone requires understanding and adhering to relevant laws and regulations. These vary by region, so it’s crucial to check your local rules before flying.
Regulations Governing Drone Operation (Example: USA)
In the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulates drone operation. Key regulations include registration requirements for drones weighing over 0.55 pounds, restrictions on flying near airports, and limitations on flight altitude and distance.
- Registration: Drones over 0.55 pounds must be registered with the FAA.
- Airspace Restrictions: Avoid flying near airports, airfields, or other restricted airspace.
- Visual Line of Sight: Maintain visual line of sight with your drone at all times.
- Altitude Restrictions: Generally, drones should not exceed 400 feet above ground level.
Obtaining Permits and Licenses
Depending on the intended use and location, obtaining permits or licenses might be necessary. The FAA’s website provides detailed information on obtaining the necessary authorizations.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Several areas are restricted to drone flights, including airports, military bases, and certain national parks. The FAA’s B4UFLY app provides real-time information on airspace restrictions.
Situations Where Drone Operation Might Be Illegal or Unethical

Flying a drone without permission over private property, flying near critical infrastructure, or using a drone for illegal activities are examples of situations where drone operation is illegal or unethical.
Successfully operating a drone involves a blend of technical understanding, responsible piloting, and adherence to regulations. By mastering the pre-flight checklist, understanding drone controls, and planning safe flights, you can unlock the exciting world of aerial perspectives. Remember to prioritize safety, continuously refine your skills, and always respect local laws and airspace restrictions. Happy flying!
Common Queries
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and beginner modes are available. Look for features like automatic return-to-home and obstacle avoidance.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved locations or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home function. If that fails, attempt to regain signal; if unsuccessful, try to visually locate the drone and recover it safely.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Flight times vary depending on the drone model and battery size, but generally range from 15 to 30 minutes.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Check your local government’s aviation authority website or the FAA website (for the USA) for specific regulations in your area.
